
Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023 — The Hindu, Page 1
GS-2: Right to Privacy | GS-3: Data Protection
Context
- Union Government notified key operational parts of the DPDP Act, 2023 along with DPDP Rules, 2025.
- Moves India towards implementing the Supreme Court’s 2017 K.S. Puttaswamy judgment (privacy = fundamental right).
- Data Fiduciaries get time till Nov 2026 to meet full compliance such as appointing a Data Protection Officer.
- Consent Manager framework for users (Data Principals) also coming into force.
2. Essential Features of the DPDP Act, 2023
A. Consent & Lawful Processing
- Clear, informed, specific consent; easy withdrawal.
- Processing must be for legitimate and stated purpose only.
- Data minimisation: collect only what is needed.
B. Rights of Individuals (Data Principals)
- Right to access their stored data.
- Right to correction and erasure.
- Right to grievance redressal.
C. Duties of Platforms (Data Fiduciaries)
- Adopt security safeguards to avoid breaches.
- Report breaches to both users and the Data Protection Board. Significant Data Fiduciaries (large platforms) must:
- Appoint Data Protection Officer
- Conduct data audits
- Undertake risk and impact assessment
D. Exemptions: Wide exemptions for State and its instrumentalities for
- national security
- public order
- law enforcement
- Relaxations for research, archiving, statistical purposes, and small entities.
E. Data Protection Board
- Independent adjudicatory body for disputes.
- Can impose penalties up to ₹250 crore for non-compliance.
F. Cross-Border Data Transfer
- Allowed only to countries notified by the Central Government.
TDF
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 seeks to reinforce the fundamental right to privacy, yet its expanded definition of personal information intensifies the conflict with the citizen’s right to information under Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act. Critically examine this emerging privacy–transparency dichotomy.(150words)
3) Issues & Criticism (w.r.t. RTI Act) :
A. Expansion of “Personal Information” → More RTI Denials
RTI: Section 8(1)(j)
- DPDP widens what counts as personal information, making it easier for departments to reject RTI queries.
- The RTI test of “larger public interest” overriding privacy becomes weaker.
B. Wider Government Exemptions
RTI: Section 24
- RTI exempts only specific security agencies.
- DPDP allows blanket exemptions to any government body → reduces scrutiny and accountability.
C. Loss of Proactive Disclosure
RTI: Section 4(1)(b)
- RTI mandates proactive publication of key govt. information.
- DPDP reduces earlier disclosure obligations → weaker institutional transparency.
D. Autonomy Concerns
- Unlike the independent Information Commissions under RTI, the Data Protection Board is appointed by the govt.
- Creates doubts about neutrality in cases involving State agencies.
1. Context:
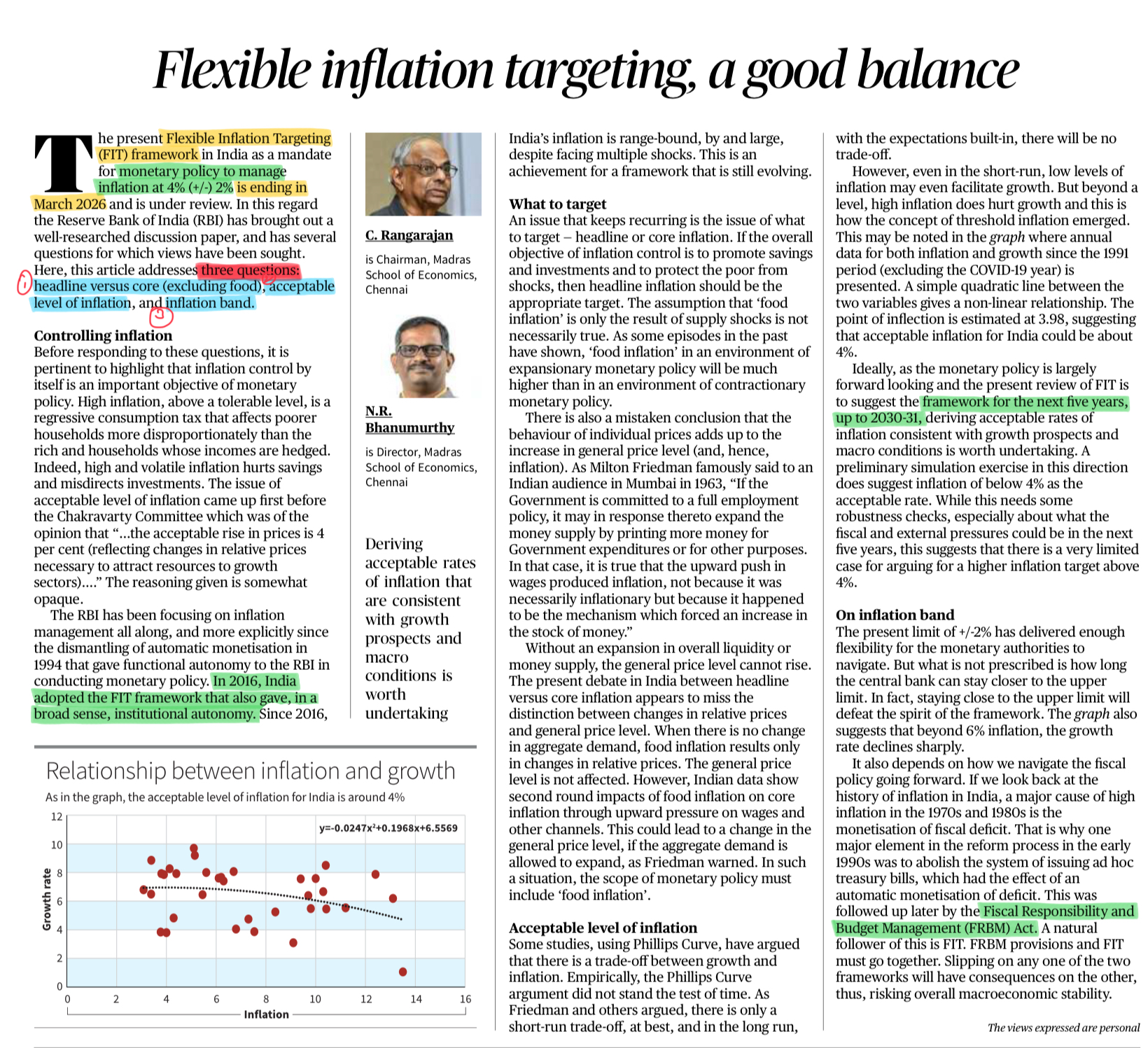
India is preparing the 2026–31 inflation-targeting framework, bringing three key questions into focus:
- Should RBI base policy mainly on headline or core inflation?
- Is 4% still the right inflation target for India?
- How much flexibility should the next framework allow to handle supply shocks and growth needs?
2. Inflation Targeting Framework (ITF)
- India follows a Flexible Inflation Targeting (FIT) system under the RBI Act (amended in 2016).
- Current target: 4% ± 2% (i.e., 2% to 6%).
- Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decides policy to keep inflation near this level.
- FIT gives RBI autonomy, but also flexibility to respond to growth concerns and supply shocks.
- The framework is revised every five years, hence the upcoming 2026–31 review.
3. Summary/Arguments
- India’s current inflation-targeting system has been effective but now requires updates.
- Headline inflation should guide policy because food–fuel fluctuations directly impact households.
- A 4% inflation target remains appropriate for India’s long-term economic structure.
- The upcoming 2026–31 framework must be flexible and practical, not rigid.
- RBI should have room to manage repeated supply shocks while still supporting growth.
- Maintaining credibility and stability should remain central to the revised framework.
4. One-Line Definitions
Headline inflation: Total inflation including food and fuel.
Core inflation: Inflation excluding food and fuel.

Context
Ambaji marble from Gujarat has been awarded a GI tag for its high-quality white stone and long-standing use in temple architecture.
Who Gives GI Tag?
• Geographical Indications Registry,
• Under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry,
• As per the GI Act, 1999.
About Ambaji Marble
• Origin: Ambaji, Banaskantha, Gujarat.
• Qualities: White, durable, high calcium, longlasting shine.
• Heritage use: 1,200–1,500 years, including Dilwara Jain Temple.
• Modern use: Temples in the U.S., New Zealand, England.

Context
PM will address Birsa Munda birth anniversary event in Gujarat and launch major tribal welfare initiatives including PM-JANMAN, DA-JAGUA, EMRS expansion, community centres, and bus services.
Key Schemes
- Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN)
• Year: 2023
• Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs
• Aim: Holistic development of PVTGs — housing, education, health, water, livelihood, road connectivity. - Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DA-JAGUA)
• Year: 2023 (State-supported initiative in tribal districts; aligned with Tribal Affairs programs)
• Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs + State Tribal Development Dept.
• Aim: Improve village infrastructure and welfare in tribal-dominated areas - Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS)
• Year: 1997 (restructured and expanded under Ministry of Tribal Affairs in 2018)
• Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs
• Aim: Provide quality residential schooling for tribal children (Class 6–12) - Multi-Purpose Community Centres (Tribal Areas)
• Year: Implemented under ongoing tribal welfare programs (State + MoTA), major expansion 2023–24
• Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs / State Tribal Development Dept.
• Aim: Act as community hubs for welfare activities, meetings, youth program

Context
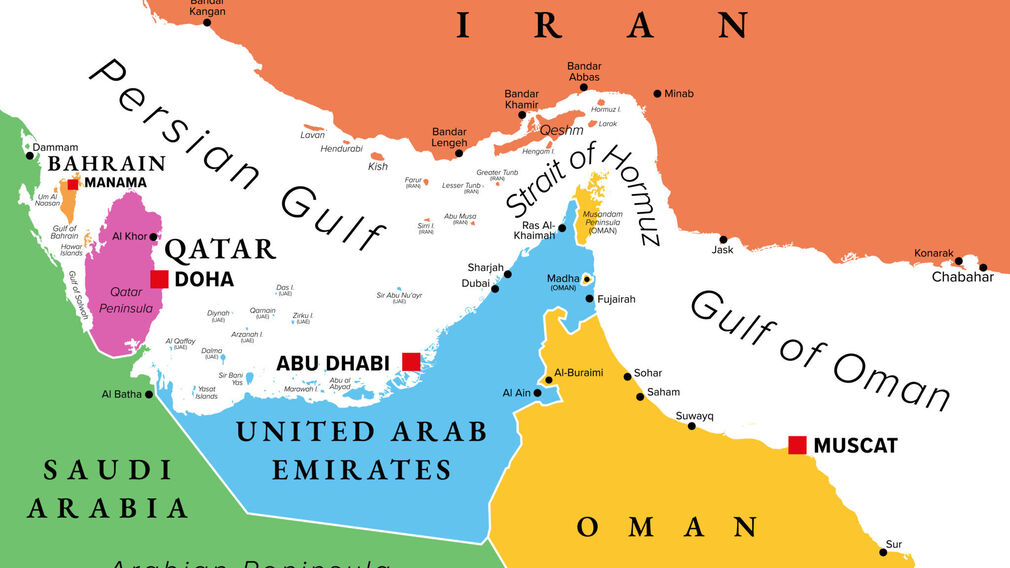
Iran intercepted a Marshall Islands–flagged oil tanker while it was passing through the Strait of Hormuz, a strategically vital maritime chokepoint for global oil transport. This incident adds to rising tensions in the region.
Strait of Hormuz
• Connects: Persian Gulf → Gulf of Oman → Arabian Sea
• Located between Iran and Oman (Musandam exclave)
• One of the world’s most critical oil chokepoints
• About 20% of global petroleum and large volumes of LNG pass through it
• Narrowest width: ~39 km
• Strategic significance: Any disruption affects global energy prices and maritime security

Context:
Pakistan’s 27th Constitutional Amendment formalises and expands the Army’s control over the state, weakening civilian authority and judicial oversight.
Main Points:
- Army Chief gains expanded powers
• New Chief of Defence Forces post, held by the Army Chief with authority over Army, Navy, Air Force.
• Legal immunity granted to top military officers. - “Hybrid Model” of Governance Becomes Formal
• Pakistan’s Army, which previously exercised power informally, now gains institutionalised authority over civilian structures.
• Civilian-led government bodies must operate within military-influenced frameworks, strengthening de facto military control. - Supreme Court Power Weakened
• The amendment effectively undermines the independence of the Supreme Court of Pakistan.
• Ensures that the judiciary cannot meaningfully challenge or review military decisions. - Foreign policy controlled by Army
• Military gains stronger control over Pakistan’s external relations and strategic partnerships.








